- Home
- Introduction
- 1. Design rights
- 1.1. Design rights: overview
- 1.2. What a design right protects
- 1.3. Why protect a design?
- 1.4. How designs are protected in Australia?
- 2. Application for registration
- 2.1. Application for registration: overview
- 2.2. Registration process
- 2.3. Submitting an application
- 2.4. Minimum filing requirements
- 2.5. Who is entitled to be a registered owner?
- 2.6. Types of applications (s 22)
- 2.7. Request for registration
- 2.8. Further designs
- 3. Fees
- 3.1. Fees: overview
- 3.2. Application fees
- 3.3. Renewal fees
- 3.4. Examination fees
- 3.5. Hearing fees
- 3.6. Fees for extensions of time
- 3.7. Refunds
- Production test Designs
- 4. Formalities assessment
- 4.1. Formalities assessment: overview
- 4.2. The ‘Formalities check’ and ‘Formal requirements’
- 4.3. Formalities notices
- 5. Applicant details
- 5.1. Applicant name: overview
- 5.1.1. Is the applicant a person?
- 5.1.2. Individual (Australian and overseas, including joint owners)
- 5.1.3. Australian company (Pty Ltd, Ltd)
- 5.1.4. Strata company, owners corporation, body corporate etc
- 5.1.5. Government entity
- 5.1.6. Incorporated association
- 5.1.7. Overseas entity (AG, S.r.L etc)
- 5.1.8. Several applicant names, multiple designs
- 5.1.9. Joint owner names with ABN
- 5.1.10. Partnership
- 5.1.11. Trust/trustee
- 5.1.12. Business names and 'trading as'
- 5.1.13. Applicant name and design owner
- 5.2. Applicant address
- 6. Representations
- 6.1. Representations: overview
- 6.2. General requirements
- 6.3. Formal compliance
- 6.4. Product
- 6.5. Consistency
- 6.6. Text
- 6.7. Common designs
- 6.8. Drawings
- 6.9. Photographs
- 6.10. Specimens or 3D models
- 6.11. Different views
- 6.12. Environmental views
- 6.13 Pairs and mirror images
- 7. Classification
- 7.1. Classification: overview
- 7.2. Classification systems
- 7.3. Finding the right class
- 7.4. Cases of doubt
- 7.5. More than one possible classification
- 7.6. Multiple products or designs
- 8. Examination and certification
- 8.1. Examination and certification: overview
- 8.2. Examination and certification processes
- 8.3. Requesting examination
- 8.4. Third party initiated examinations
- 8.5. Concurrent requests for examination
- 8.6. Expedited examination
- 8.7. Material provided by a third party
- 8.8. Relevant material that must be considered
- 8.9. Time frame for completion of examination and last-minute responses
- 8.10. Withdrawal of request for examination
- 8.11. Notice of intention to certify
- 8.12. Requests for examination after certification
- 8.13. Further examination reports
- 8.14. Revocation
- 8.15. Examination hearings
- 8.16. Examination on Registrar's initiative
- 9. Identifying the design
- 9.1. Identifying the design: overview
- 9.2. Overall appearance
- 9.3. Visual features
- 9.4. Variable visual features
- 9.5. What cannot be a visual feature
- 10. Product
- 10.1. Product: overview
- 10.2. Identifying the product
- 10.3. Things that are not products
- 10.4. Things that are not different products
- 10.5. Product name
- 10.6. Manufactured or handmade
- 10.7. Component part of a complex product
- 10.8. Assembled set or kit
- 10.9. Indefinite dimensions
- 10.10. Examples - things that are / are not products
- 11. Excluded designs
- 11.1. Excluded designs: overview
- 11.2. Priority date of excluded designs
- 11.3. Extensions of time
- 11.4. Amendments
- 11.5. Registration/publication requests
- 12. Section 43 refusal to register
- 12.1. Section 43 refusal to register: overview
- 12.2. Medals
- 12.3. Anzac
- 12.4. Currency
- 12.5. Scandalous content
- 12.6. Arms, flags, emblems etc.
- 12.7. Olympic symbols
- 12.8. Integrated circuits
- 13. Assessing newness and distinctiveness
- 13.1. Assessing newness and distinctiveness: overview
- 13.2. Product name and intended use
- 13.3. Identifying the product
- 13.4. Test for newness
- 13.5. Test for distinctiveness
- 13.6. Substantially similar in overall impression
- 13.7. How the design is displayed
- 13.8. Other visual features
- 13.9. Searching
- 14. Section 19 requirements for distinctiveness
- 14.1. Section 19 requirements for distinctiveness: overview
- 14.2. Similarities and differences
- 14.3. State of development of the prior art base
- 14.4. Statement of newness and distinctiveness
- 14.5. Amount, quality and importance
- 14.6. Freedom of the creator of the design to innovate
- 14.7. Familiar person / Informed user
- 15. Statement of newness and distinctiveness
- 15.1. Statement of newness and distinctiveness: overview
- 15.2. Formalities assessment of the SoND
- 15.3. Amendments to the SoND
- 15.4. Using the SoND to assess distinctiveness
- 16. Standard of the familiar person / informed user
- 16.1. Standard of the familiar person / informed user: overview
- 16.2. Identifying the familiar person / informed user
- 16.3. Declarations about the familiar person / informed user
- 16.4. Familiarity with the product
- 16.5. References to European and UK decisions
- 16.6. Familiar person’s / informed user’s knowledge base versus prior art base
- 17. Prior art base
- 17.1. Prior art base: overview
- 17.2 Publicly used in Australia
- 17.3. Published in a document within or outside of Australia
- 17.4. Trade marks and patents as citations
- 17.5. Establishing the publication date
- 17.6. Designs disclosed in applications
- 18. Prior publication or use exceptions
- 18.1. Prior publication or use exceptions: overview
- 18.2. Exhibitions
- 18.3. Unauthorised disclosures
- 18.4. Disclosure to government
- 18.5. Copyright
- 18.6. Grace Period
- Annex A - An example of a grace period declaration
- 19. Priority date
- 19.1. Priority date: overview
- 19.2. Convention application
- 19.3. Multiple bases for priority
- 19.4. Plural designs
- 19.5. When priority must be asserted
- 19.6. Excluded designs
- 19.7. Converted applications
- 19.8. Applications by an entitled person
- 20. Convention priority
- 20.1. Convention priority: overview
- 20.2. Convention countries
- 20.3. Time limit to claim convention priority
- 20.4. Assessing convention priority claims
- 20.5. Convention priority for excluded designs and applications that include more than one design
- 20.6. Basic application
- 20.7. Requesting the basic application
- 20.8. Relevance of the basic application to examination
- 21. Satisfied
- 21.1. Satisfied: overview
- 21.2. Meaning of ‘satisfied’
- 21.3. ‘Satisfied’ as to prior art base
- 21.4. Reasonable doubt, balance of probabilities and uncertainty
- 21.5. ‘Not satisfied’
- 22. Amendments
- 22.1. Amendments: overview
- 22.2. Amending an application
- 22.3. Amending a registration
- 22.4. Inclusion of matter not in substance disclosed
- 22.5. Increasing the scope of the design registration
- 22.6. Other types of amendments
- 23. Extensions of time
- 23.1. Extensions of time: overview
- 23.2. Legal principles
- 23.3. Error or omission by the Registrar
- 23.4. Error or omission by the customer
- 23.5. Circumstances beyond the customer’s control
- 23.6. Registrar’s discretion
- 23.7. Protection for third parties
- 23.8. Period of extension
- 23.9. Extensions process
- 23.10. Advertisement
- 23.11. Request from an unrecorded new owner
- 23.12. Extension of the convention priority period
- 24. Assignments (and other interests)
- 24.1. Assignments and other interests: overview
- 24.2. Recording changes of ownership
- 24.3. Possible complications
- 24.4. Bankruptcy and winding up
- 24.5. Registering other interests
- 25. Ownership disputes
- 25.1. Ownership disputes: overview
- 25.2. Disputes between joint applicants
- 25.3. Disputes where a non-applicant claims ownership
- 25.4. Disputes where some designs have been registered or published
- 25.5. Disputes about recording a change of ownership before registration
- 25.6. Typical situations where ownership disputes arise
- 25.7. Revocation after an ownership dispute
- 26. Production of documents under s 61(1)
- 26.1. Production of documents under s 61(1): overview
- 26.2. Powers of the courts
- 26.3. Powers of the Registrar
- 26.4. Precedent
- 26.5. Who access is granted to
- 26.6. Access in ownership disputes
- 26.7. Where inspection can take place
- 26.8. Right of lien
- 26.9. Draft undertaking for access
- 27. Publication and file access
- 27.1. Publication and file access: overview
- 27.2. Designs not publicly available
- 27.3. Legal exceptions
- 27.4. Freedom of information
- 27.5. Prohibition orders
- 28. Hearings
- 28.1. Hearings: overview
- 28.2. Filing evidence
- 28.3. Disputes over whether the design was new and distinctive at the priority date
- 28.4. Interface with court proceedings
- 29. Glossary
- 30. Citation index
- 31. Keyword index
- 32. Classification listings
- Class Heading Summary
- Class 01 Foodstuffs
- Class 02 Articles of clothing and haberdashery
- Class 03 Travel goods, cases, parasols and personal belongings not elsewhere specified
- Class 04 Brushware
- Class 05 Textile piecegoods, artificial and natural sheet material
- Class 06 Furnishing
- Class 07 Household goods not elsewhere specified
- Class 08 Tools and hardware
- Class 09 Packages and containers for the transport or handling of goods
- Class 10 Clocks and watches and other measuring instruments, checking and signalling instruments
- Class 11 Articles of adornment
- Class 12 Means of transport or hoisting
- Class 13 Equipment for production, distribution or transformation of energy
- Class 14 Recording, communication or information retrieval equipment
- Class 15 Machines not elsewhere specified
- Class 16 Photographic, cameras, cinematographic and optical apparatus
- Class 17 Musical instruments
- Class 18 Printing and office machinery
- Class 19 Stationery and office equipment, artists and teaching materials
- Class 20 Sales and advertising equipment, signs
- Class 21 Games, toys, tents and sporting goods
- Class 22 Arms, pyrotechnic articles, articles for hunting, fishing and pest killing
- Class 23 Fluid distribution equipment, sanitary, heating, ventilation and air conditioning equipment, solid fuel
- Class 24 Medical and laboratory equipment
- Class 25 Building units and construction elements
- Class 26 Lighting apparatus
- Class 27 Tobacco and smokers supplies
- Class 28 Pharmaceutical and cosmetic products, toilet articles and apparatus
- Class 29 Devices and equipment against fire hazards, for accident prevention and rescue
- Class 30 Articles for the care and handling of animals
- Class 31 Machines and appliances for preparing food or drink, not elsewhere specified
- Class 32 Graphic symbols and logos, surface patterns, ornamentation
- 33. Designs (Formal Requirements for Designs Documents) Instrument 2022
22.4. Amendments: Inclusion of matter not in substance disclosed
Under both s 28 and s 66 of the Designs Act 2003, an amendment to a design is not allowable if it would “alter the scope” of the [application / registration] by the inclusion of matter that was not in substance disclosed in the design application, representations, or any other document filed as part of the original application.
This restriction is limited to matter that defines the design. This includes the product name and representations. This does not apply to other particulars, where the scope of the actual design is not affected. For example, applicant / owner personal detail, convention detail.
In substance disclosed
“In substance disclosed” typically means the explicit disclosure of detail (in the design application, representations, or any other document originally filed). However, the absence of explicit detail does not necessarily mean that detail was not “in substance disclosed”.
The meaning of "in substance disclosed", as distinct from an explicit disclosure, has previously been considered in a patents context. In A.B. Volvo's Application (1983) 1 IPR 554, reference was made to the following High Court statement:
‘The substance must appear from the language itself interpreted in accordance with ordinary rules of interpretation with a knowledge of the prior state of the art to which the claim relates.’ (AMP Incorporated v Commissioner of Patents (1974) AOJP 3224)
In a designs law context, the substance will usually appear from the representations, based on similar principles.
Matter that was not explicitly disclosed can potentially be introduced by amendment. Amendment requests that are reasonable and genuine in terms of scope can be allowed. Chris Ford Enterprises Pty Ltd v. B. H. & J. R. Badenhop Pty Ltd (1985) 4 IPR 485 at 498 concluded [in respect of s 22B of the Designs Act 1906 (Cth)]:
‘It would seem that it is designed to exclude amendments which extend the scope in some fundamental way and make disclosures clearly beyond those already made. The terms of S22B(1A) are in a sense imprecise and call for the exercise of judgement. Reading the section as a whole it is proper to conclude that parliament intended genuine amendments reasonable in scope should be permissible and that the restrictive provision of S22B(1A) should be interpreted accordingly.’
Guidance on what is a ‘genuine amendment reasonable in scope’ may be ascertained from Ethyl Corporation's Patent (1972) RPC 169:
'Disclosed in substance' means either expressly disclosed or impliedly disclosed. Impliedly disclosed means that it would be implied by the informed user.
To put these decisions into the context of designs, the matter should appear from the original design application, representation, or other documents, be interpreted in a normal way and from the perspective of person(s) familiar with the product (to which the design applies).
To introduce matter not made explicit in the original design application, representation, or other documents requires it to be interpreted in a normal way, and to be matter that person(s) familiar with the product ordinarily expects to be originally included or would understand as being originally introduced. For example, an amendment that makes explicit details that person(s) familiar with the product necessarily imply from the representations.
Designs disclosed in other applications
If an applicant applies for an amendment based on a design that was disclosed in a different application, and the design has not been registered or published, the material must be placed on the current file and made available to the public where relevant.
An example of this scenario is an amendment request for an excluded design registration where the proposed design was originally disclosed in the initial application from which the excluded design is derived.
Also, where an original design application contains further designs, the ‘in substance disclosed’ element covers disclosure in all those designs, even where the files of the other design applications are not open to public inspection.
Time restriction on disclosure
There is no time restriction on the use of disclosure in requesting an amendment. For example, a disclosure in a covering letter could be used as the basis for an amendment request many years after registration and certification.
Examples
Example 1 (Design 202110049)
The product name is ‘Espresso coffee machine’. The representation shows a standard coffee machine:
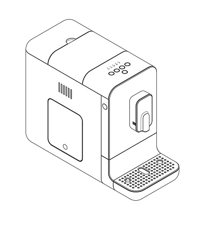
There is a request to amend the representation to include a coffee machine with integrated milk frother and amend the product name accordingly. The request includes matter not in substance disclosed, resulting in an unacceptable altering of the scope of the application.
Example 2
An amendment request is received that seeks to amend solid line detail, included as part of the original design representations, to broken line detail. This amendment would be allowable as the change does not alter the scope of the design by introducing new matter. The line detail was in substance disclosed in the original application. The effect of the amendment is limited to the amount of emphasis placed on the line detail when assessing newness and distinctiveness if examination (of the registered design) occurs.
This type of amendment may also be requested under s 66. Whilst it may not fall foul of s 66(6)(b), it may be problematic when considering the other conditions that must be met to amend a design registration.
Amended Reasons
| Amended Reason | Date Amended |
|---|---|
Minor correction. |
|
Example update. |
|
Amendments review. |
